The Cultural Legacy of Rome
Selected dates:
209 BCE Beginning of Roman Conquest of Iberia (or Hispania) as the Romans called it.
178 BCE The native Iberians are defeated by the Romans and Iberia becomes an important center of the Roman Empire.
133 BCE: The inhabitants of Numantia prefer to die rather than surrender to the Roman general Scipio Aemilianus.
27 BCE: The Romans
pacify the
19 BCE: The Roman emperor Augustus (r. 27 BCE-14CE) completes the conquest of Spain.
98 CE: The rule of Trajan, the first Roman emperor of Spanish origin, begins. The emperors Hadrian (r. 117-38), and Marcus Aurelius (r. 161-80) also were born in Spain .
312 CE Emperor Constantine becomes a Christian.
330 CE Constantine establishes the city of Constantinople, the first Christian city and for a time center of the early Church. Constantinople fell in 1453.
354 CE St. Augustine born in North Africa of a pagan father and Christian mother. In 387 CE he converts to Christianity.
380 CE Christianity is proclaimed the sole religion of the Roman Empire by Theodosius I.
395 CE Death of Theodosius. The empire is divided between his sons, Arcadius in the East, and Honorius in the West. This is the end of Imperial unity; the East, which is called Byzantium is now autonomous.
399 CE St. Augustine (d. 430) is elected Bishop of Hippo. His Confessions is the first autobiography in western history. His most famous work, The City of God unites the sacred history of the Jewish people, the pagan history of the Greeks and Romans, and the Christian expectation of future salvation. He quotes classical writers such as Plato, Cicero, Seneca and Aristotle, the Old and New Testaments, and the interpretations and commentaries of the Church Fathers.
407-09 CE The Alans, Vandals, and Suevi cross a frozen Rhine and run through Gaul and Spain. They settle in Spain in 409. See table for more details.
410 CE The Visigoths (a Germanic people believed to have come from what is now Sweden) and their German allies sack Rome.
415 CE The Visigoths arrive and establish their kingdom in Northeast Spain.
416 CE The Visigoths break up the kingdoms of the Alans, Vandals and Suevi.
429-35 CE The Vandals move across Spain into North Africa.
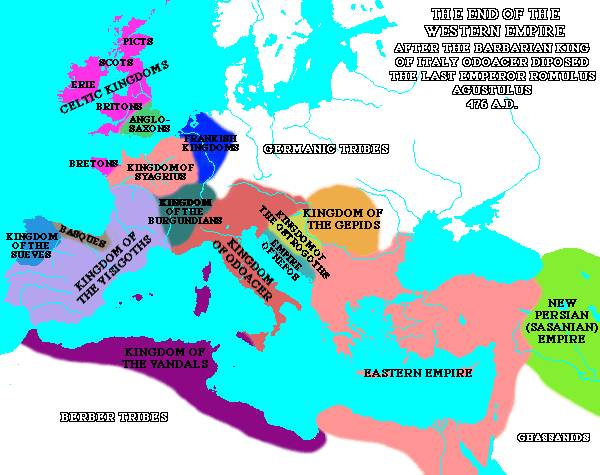
476 CE Odovacer, the leader of the united German tribes, assumes the title of king of Rome. This date is commonly used to signal the end of the Western Roman Empire and after it there are no Roman Emperors occupying the West at all.
527 CE Visigoths make Toledo their capital.
By the end of the 6th century THREE ELEMENTS basic to western civilization in the Middle Ages are in place:
GRAECO-ROMAN CULTURE
THE CHRISTIAN CHURCH
THE GERMANIC PEOPLES AND THEIR INSTITUTIONS

Map from http://historicist.tripod.com/ch8.htm
Rome's legacy:
I. Construction of roads, bridges, acqueducts: Segovia, Italica, Merida and Cordoba
II. Linguistic- Development of the Romance languages
|
Linguistic Relationships among Romance Languages |
||||||
|
English |
Latin |
Portuguese |
Spanish |
French |
Italian |
Romanian |
|
black |
|
negro |
negro |
noir |
nero |
negru |
|
do |
facere |
fazer |
hacer |
faire |
fare |
face |
|
green |
viridis |
verde |
verde |
vert |
verde |
verde |
|
horse |
caballus |
cavalo |
caballo |
cheval |
cavallo |
cal |
|
iron |
ferrum |
ferro |
hierro |
fer |
ferro |
fier |
|
three |
tres |
tręs |
tres |
trois |
tre |
trei |
From: http://www.infoplease.lycos.com/ce6/society/A0829878.html
| Latin/Vernacular | Written/Oral | Learned/ Popular |
Examples
England: Latin- French- English (after the Norman Conquest)
Spain: Latin-Vernacular (romance)
Arabic-Hebrew-Vernacular (Mozarabic)
III. Continuance of Classical Culture (select examples). Major roman contributions in government, law, engineering, rhetoric, and literature
Philosophy: Classical philosophy of Greece and Rome: Plato (427-348 BC), Aristotle ((384 - 322 BC), Seneca the Younger (ca. 4 BC in Cordoba, Spain-65 CE; Roman Stoic philosoher)
Religion: Formation of the Early Christian Church. The "Church Fathers" (Jerome, Ambrose and Augustine are major figures)
History: Plutarch (c. 46- 127 CE; Greek historian, biographer, and essayist), Livy (59 BCE-17 CE; wrote a monumental history of Rome)
Law: 'Justinian Code'. This code formed by the Emperor Justinian in the 6th century became the basis of all systems of law in the western world.
Rhetoric, Literature: Ovid (Greece), Lucan (39 CE, in Córdoba], Spain-65 CE; Roman poet), Cicero (106 BCE-43 BCE; orator, statesman, political theorist, lawyer and philosopher), Virgil (70-19 BC; the author of epics such as the Aeneid)
IV. Terms:
Christian: followers of Christianity
Muslim: followers of Islam (many different ethnic groups such as the Arabs and the Berbers)
Moor: Muslims of the Iberian Peninsula
Mozarab: Christians living under Islamic rule
Mudejar: Muslims living under Christian rule
Names referring to the Peninsula: Iberia (Greeks), Hispania (Romans), Al-Andalus (Arabs), Sepharad (Jews)